Understanding the Automobile Braking System

The automobile braking system is an essential component of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control through effective deceleration. This complex system transforms kinetic energy into heat, thus slowing down the vehicle and providing an indispensable function in traffic and road safety.
What is the Automobile Braking System?
The automobile braking system is designed to slow down or stop the vehicle when pressure is applied to the brake pedal. It consists of various components, including:
- Brake Pedal - The driver’s interface that initiates braking.
- Brake Booster - A device that amplifies the force applied to the brake pedal.
- Brake Fluid - A hydraulic fluid that transmits pressure from the pedal to the brakes.
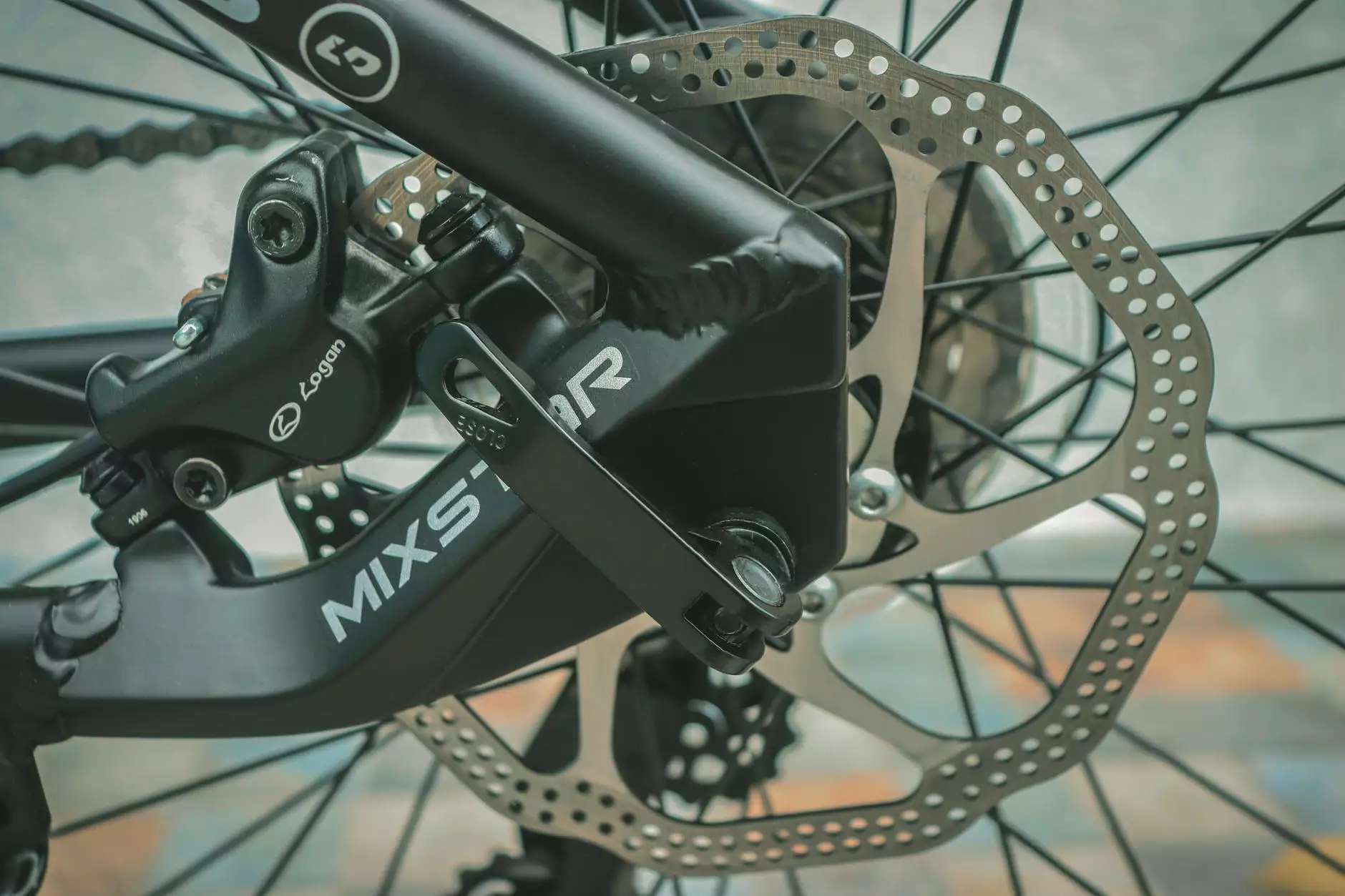
- Brake Calipers - Mechanisms that hold the brake pads and apply them to the rotor.
- Brake Pads - Friction material that clamps down on the rotor to stop the vehicle.
- Brake Rotors - Disc components that rotate with the wheels and are clamped by the pads.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) - A safety feature that prevents wheel lock-up during braking.
How Does an Automobile Braking System Work?
When the driver presses the brake pedal, a sequence of events is triggered:
- The brake pedal pushes a rod which activates the brake booster.
- The brake booster increases the force sent to the master cylinder.
- Brake fluid is pushed through the brake lines to the calipers.
- The calipers push the brake pads against the rotors.
- This friction generates heat, slowing the vehicle.
Types of Automobile Braking Systems
There are two primary types of braking systems used in most automobiles:
1. Disc Braking System
The disc braking system uses brake pads that squeeze against a brake disc (rotor) mounted on the wheel. This type of braking system is preferred for its superior performance in heat dissipation and stopping power. Key benefits include:
- Improved braking performance under heavy loads.
- Reduced brake fade compared to drum systems.
- Enhanced wet-weather performance.
2. Drum Braking System
The drum braking system consists of brake shoes pressed against the inner surface of a drum. Though an older design, it still has applications, especially in rear brakes. Advantages include:
- Cost-effectiveness in mass production.
- Good performance in light-duty applications.
Components of the Automobile Braking System
Understanding the individual components of a braking system helps appreciate its complexity and importance:
Brake Pads
Brake pads are engineered from materials designed to withstand heat and friction. They come in various types, including:
- Organic Pads - Made from materials such as rubber and resin, offering good performance for light vehicles.
- Metallic Pads - Made from metallic fibers, they offer superior performance but can be noisier.
- Semi-metallic Pads - A blend of metal and organic materials, they provide a balance of performance and noise reduction.
Brake Calipers
Brake calipers are critical for the operation of disc brakes. They house the brake pads and are responsible for applying pressure to them. There are two primary types of calipers:
- Floating Calipers - These move in and out relative to the rotor.
- Fixed Calipers - These have pistons on both sides of the rotor, providing enhanced clamping force.
Brake Fluid
Brake fluid is essential for hydraulic pressure in the braking system. Its properties must endure high heat and pressure, making it critical to use the right type as specified in the owner's manual.
Maintenance of the Automobile Braking System
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the reliability of the automobile braking system. Here are key maintenance tips:
1. Regular Inspections
Checking brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels can help spot potential issues before they lead to total system failure.
2. Brake Pad Replacement
The lifespan of brake pads varies but typically ranges from 30,000 to 70,000 miles. Factors such as driving style and vehicle type can influence longevity. Look for signs of wear including:
- Squeaking or grinding noises.
- Vibration during braking.
- Warning lights on the dashboard.
3. Check Brake Fluid
The brake fluid should be checked regularly to ensure it is at the proper level and free of contaminants. Change the brake fluid every 2 years or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Innovations in Automobile Braking Systems
The automotive industry continually integrates advanced technologies into braking systems. Significant innovations include:
1. Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
ABS prevents wheel lock-up during hard braking, enhancing vehicle control. It automatically modulates pressure to the brakes, allowing for steering control.
2. Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
ESC works with the braking system to prevent skidding during sudden turns. It automatically applies brakes to individual wheels to maintain vehicle stability.
The Future of Automobile Braking Systems
Looking forward, innovations like regenerative braking systems in electric and hybrid vehicles present exciting prospects for the future of the automobile braking system. This technology captures energy during braking to recharge the vehicle's battery, promoting efficiency and sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the automobile braking system is a topic of utmost importance for vehicle safety and performance. An understanding of its components, functionality, and maintenance will not only enhance your automotive knowledge but also contribute significantly to safe driving practices. By staying informed through resources like imautoparts.com, you can ensure that your vehicle remains safe and efficient on the road.
For any needs related to automotive parts or supplies, visiting imautoparts.com will provide you with valuable resources and high-quality products to keep your vehicle's braking system in excellent condition.